Arthritis in the lower back, medically known as lumbar spine arthritis or lumbar spondylosis, is a common cause of chronic back pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, especially in adults over 40. It develops gradually due to wear and tear of the joints, discs, and cartilage in the lower spine. While the condition cannot be completely reversed, many people wonder, “What is the best treatment for arthritis in the lower back?” The focus of effective treatment is on pain control, maintaining movement, and preventing progression.
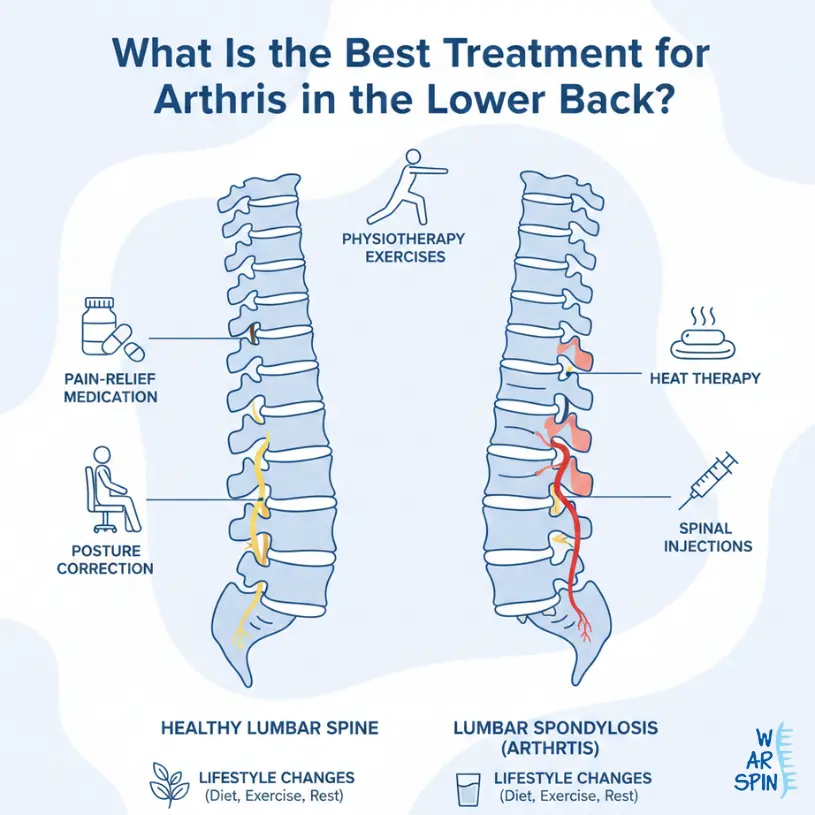
Understanding Arthritis in the Lower Back
The lower back contains five lumbar vertebrae supported by facet joints and intervertebral discs. In arthritis, these joints undergo degeneration, leading to:
- Loss of cartilage
- Inflammation of joints
- Formation of bone spurs (osteophytes)
- Reduced joint flexibility
This process causes pain, stiffness, and sometimes nerve compression.
What Is the Best Treatment for Arthritis in the Lower Back?
There is no single “one-size-fits-all” treatment. The best treatment for arthritis in the lower back depends on:
- Severity of symptoms
- Level of joint degeneration
- Presence of nerve compression
- Age and activity level
Most patients improve significantly with non-surgical treatments, while surgery is reserved for severe cases.
1. Lifestyle Modification and Activity Management
Key changes include:
- Avoiding prolonged sitting
- Maintaining correct posture
- Using lumbar support while sitting
- Avoiding sudden twisting or heavy lifting
2. Physiotherapy and Targeted Exercises
How physiotherapy helps:
- Strengthens core and back muscles
- Improves spinal flexibility
- Reduces stiffness
- Enhances joint stability
Common physiotherapy components include:
- Core strengthening exercises
- Gentle stretching
- Postural training
- Heat or ultrasound therapy
3. Pain Relief Medications (Short-Term Use)
Commonly prescribed options:
- Paracetamol for mild pain
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Muscle relaxants for spasms
4. Weight Management
Benefits of weight control:
- Reduces load on lower back joints
- Decreases pain intensity
- Improves mobility
5. Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy are simple but effective supportive treatments.
- Heat therapy helps relax muscles and reduce stiffness
- Cold therapy reduces inflammation and numbs acute pain
6. Posture Correction and Ergonomic Support
Helpful measures include:
- Ergonomic chairs with lumbar support
- Proper desk height
- Sleeping on a supportive mattress
- Avoiding slouched sitting positions
7. Injections for Persistent Pain
Common options include:
- Facet joint injections
- Epidural steroid injections
8. When Is Surgery Considered?
Surgery is not the first-line treatment for arthritis in the lower back. It is considered only when:
- Pain is severe and persistent
- Nerve compression causes weakness or numbness
- Daily activities become significantly restricted
- Conservative treatments fail over several months
When to See a Spine Specialist
Consult a spine specialist if you experience:
- Persistent lower back pain lasting more than a few weeks
- Pain radiating to the legs
- Numbness or weakness
- Difficulty walking or standing
Final Thoughts
So, what is the best treatment for arthritis in the lower back?
The most effective approach is a combination of physiotherapy, lifestyle modification, posture correction, and controlled pain management, with injections or surgery reserved for more severe cases.
Managing lower back arthritis is a long-term process, but with the right care plan, most patients can lead active, independent, and pain-controlled lives. If symptoms are affecting your quality of life, seeking timely medical advice is the most important first step.
Struggling with persistent back pain? Sometimes it’s the little things we do every day that make a huge difference. Don’t miss our quick video on 5 daily habits that could be affecting your back health: